Software Dev Process Lecture Notes - Part 3 Lesson 3 - Design Patterns
Software Design Patterns
History of Patterns
- Prof discusses brief history of the people who came up with and developed the idea of reusable idioms in software dev. Culminates in mention/endorsement of the Gang of Four book.
Design patterns
-
Shows eye chart of many different patterns, of different types. Indicates we will review just a couple of them in depth for this lesson.
-
Format of pattern (subset)
- How do you actually define a pattern?
- NAme, Intent, Motivation, Applicability, Structure, consequences, Implementation, Sample Code, Related Patterns, and much more (tm).
- For this lesson, we will look at only name, intent, applicability, structure, and sample code.
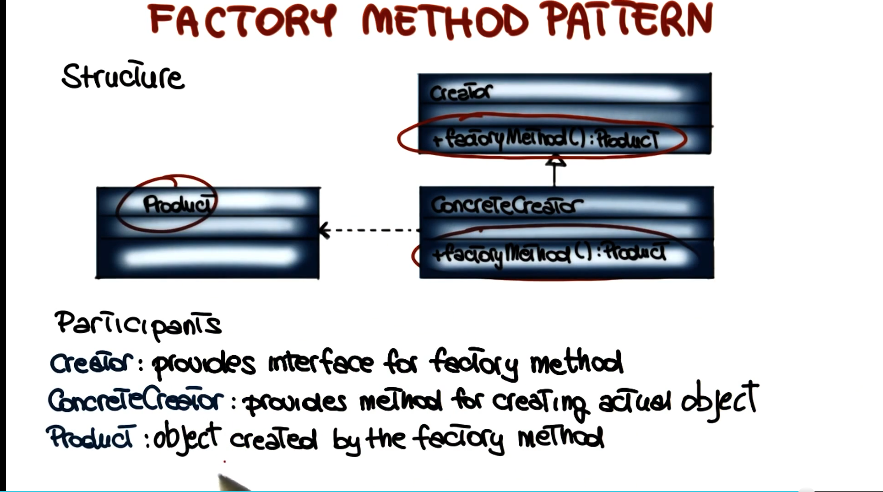
Factory Method Pattern
- Intent
- Allows for creating objects without specifying their class, by invoking a factory method (i.e. a method whose main goal is to creata class instances)
- Applicability
- Class can’t anticipate the type of objects it must create
- Class wants its subclasses to specify the type of objects it creates
- Class needs control over the creation of its objects
- Sample Code
public class ImageReaderFactory { public static ImageReader createImageReader(InputStream is) { int imageType = getImageType(is); switch (imageType) { case ImageReaderFactory.GIF return new GifReader(is); case ImageReaderFactory.JPEG return new JpegReader(is); //... } } }
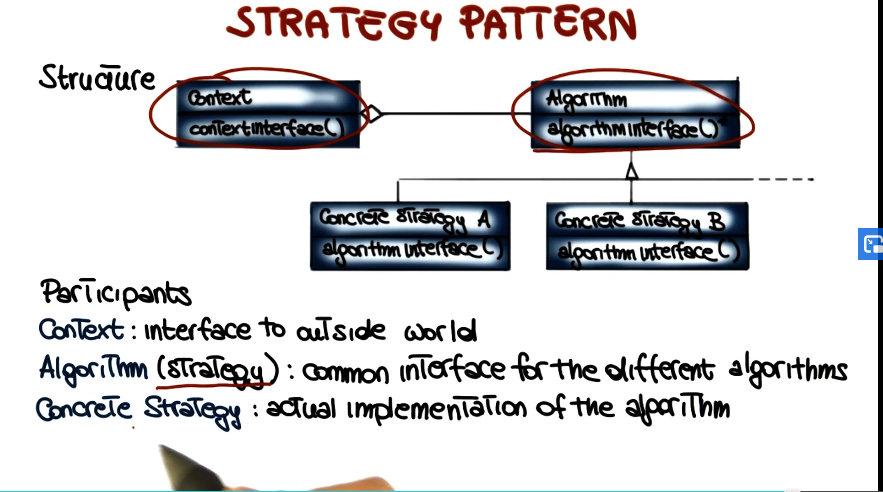
Strategy Pattern
- Intent
- Allows for switching between different algorithms for accomplishing a task
- Applicability
- Different variants of an algorithm
- Many related classes differ only in their behavior
- Example
- Program
- Input: text file
- Output: filtered file
- Four filters
- No filtering
- only words that start with “t”
- only words longer than 5 characters
- only words that are palindromes
- Program
- Sample Code ``` //Algorithm interface interface CheckStrategy { public boolean check(String s); }
//Algorithm instances class All implements CheckStrategy { @Override public boolean check(String s) { return true; } }
class StartWithT implements CheckStrategy { @Override public boolean check(String s) { if( s == null || s.length() == 0) { return false; } return s.charAt(0) == ‘t’; } }
class LongerThan5 implements CheckStrategy { @Override public boolean check(String s) { if(s == null) { return false; } return s.length() > 5; } }
class Palindrome implements CheckStrategy { @Override public boolean check(String s) { if(s == null) { return false; } int length = s.length(); if(length < 2) { return true; } int half = length/2; for(int i = 0; i < half; ++i) { if(s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(length - 1 - i)) { return false; } } return true; } }
class Context { private CheckStrategy strategy;
public Context() {
this.strategy = new All();
}
public void changeStrategy(CheckStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public void filter(String filename) throws IOException {
BufferedReader infile = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
String buffer = null;
while((buffer = infile.readLine()) != null) {
StringTokenizer words = new StringTokenizer(buffer);
while( words.hasMoreTokens() ) {
String word = words.nextToken();
if (strategy.check(word)) {
System.out.println(word);
}
}
}
} }
public class StrategyPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Context context = new Context();
String filename = "foo.txt";
System.out.println("\n* Default:");
context.filter(filename);
System.out.println("\n* Longer than 5:");
context.changeStrategy(new LongerThan5());
context.filter(filename);
System.out.println("\n*Palindromes:");
context.changeStrategy(new Palindrome());
context.filter(filename);
} }
```
Other Common Patterns
- Visitor
- A way of separating an algorithm from an object structure on which it operates
- Decorator
- A wrapper that adds functionality to a class: stackable!
- Iterator
- Access elements of a collection without knowing underlying representation
- Observer
- Notify dependents when object changes
- Proxy
- Surrogate controls access to an object
Choosing a Pattern
- Approach
- Understand your design context
- Examine the patterns catalogue
- Identify and study related patterns
- Apply suitable pattern
- Pitfalls
- Selecting wrong patterns
- Abusing patterns (astronaut behavior)
Negative Design Patterns
- How not to do things
- Also called anti-patterns and bad smells